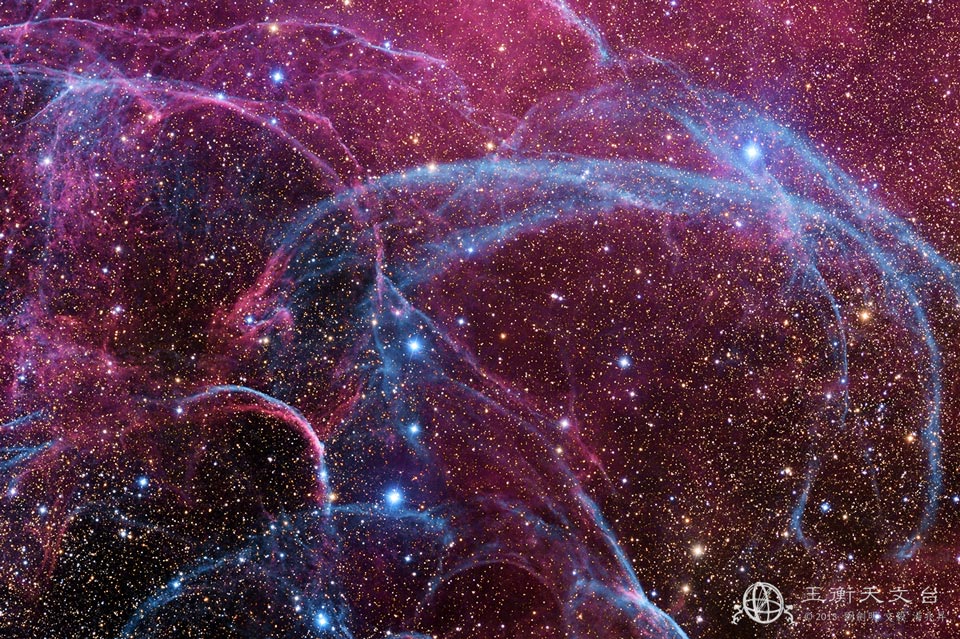

2013年10月01日:船帆座超新星遗骸的云气丝-(Filaments of the Vela Supernova Remnant)--原图下载
Image Credit & Copyright: Angus Lau, Y Van, SS Tong (Jade Scope Observatory)
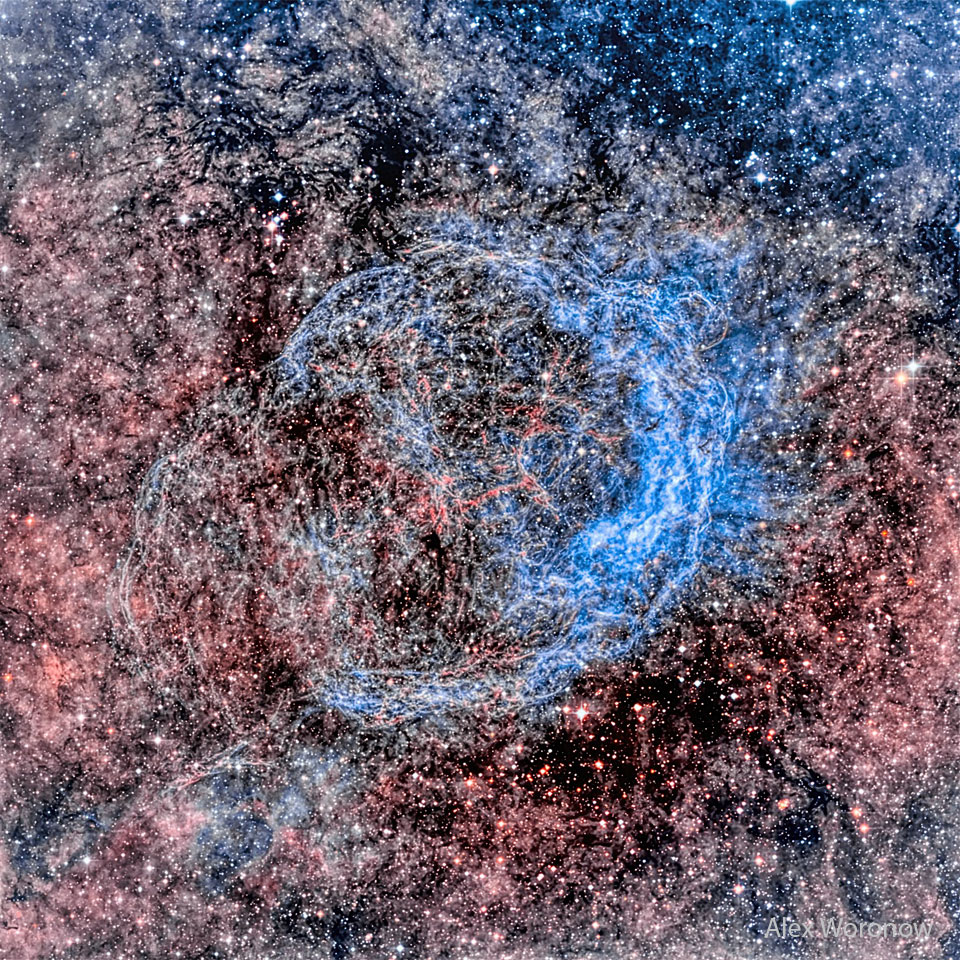
说明: 爆炸已结束,但其影响仍持续着。约在1万1千年前,在人类刚开始记载历史之时,船帆座有一颗星发生爆炸,在天空中形成一个短暂可见的奇异光点。 这颗星的外层冲撞星际物质,所产生的冲击波至今仍然可见;尤其在在X光波段,可清楚见到这道几乎是球状的扩张冲击波。上面这张照片,在可见光波段捕捉到部份的庞大冲击波和云气丝。当气体从爆炸的恒星飞离时,它会发生衰变并和星际物质发生反应,产生各种颜色和波段的光。在船帆座超新星遗骸的中心有颗脉冲星,它是一颗緻密度如同核物质的天体,而且每一秒自转十次以上。
原文:
Image Credit & Copyright: Angus Lau, Y Van, SS Tong (Jade Scope Observatory)
Explanation: The explosion is over but the consequences continue. About eleven thousand years ago a star in the constellation of Vela could be seen to explode, creating a strange point of light briefly visible to humans living near the beginning of recorded history. The outer layers of the star crashed into the interstellar medium, driving a shock wave that is still visible today. A roughly spherical, expanding shock wave is visible in X-rays.The above image captures some of that filamentary and gigantic shock in visible light.As gas flies away from the detonated star, it decays and reacts with the interstellar medium, producing light in many different colors and energy bands.Remaining at the center of the Vela Supernova Remnant is a pulsar, a star as dense as nuclear matter that rotates completely around more than ten times in a single second.





评论